メタノールなどの液体燃料は水素などに比べると格段にエネルギー密度が高く、それを効率良く電力に変換することで長時間の発電が可能になります。装置の仕組みを簡単化した携帯電子機器用の小型の発電装置も可能です。これは移動体やロボットなどの電源システムにも適していると期待されます。将来、メタノールは回収した二酸化炭素を原料にして作られるエネルギーキャリアとも目されており、直接メタノール燃料電池(DMFC)の性能が上がれば様々な用途での利用が期待されます。当研究室ではDMFCにおいて従来では使用が難しかった、高濃度燃料の使用を可能とする電極構造を提案し、この構造を用いたDMFCスタックのプロトタイプの開発に成功しました。直接メタノール型燃料電池では、燃料のメタノールが反応しないまま空気極側に漏れ出すことが大きな問題となっていました。その結果、低濃度のメタノールしか利用できなかったり、稀釈のための複雑なシステムが必要になったりして、燃料電池から取り出せる電力が小さくなっていました。本研究室では特殊な多孔質板を用いた電極構造により、メタノールの透過速度を調整して、メタノール透過損失を無くし、100%の高濃度のメタノールでも効率よく利用できるようにしました。このDMFCでは、これまでよりも簡単なシステム構造で長時間駆動可能な燃料電池システムを構築できます。
The direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) is suitable for high-power portable and stationary applications due to the high energy density and easy handling of methanol. In DMFC, mass transport of substances such as water, methanol, and carbon dioxide through electrodes and/or electrolyte membranes strongly affects the power generation characteristics. In particular, the permeation of methanol through the electrolyte membrane greatly reduces the power generation efficiency, so it was difficult to use high-concentration methanol in DMFC. We have proposed a novel electrode with a porous plate which enables the use of high-concentration methanol solution. We have succeeded in developing a DMFC prototype which can be operated by a high concentration methanol solution as high as 100%.
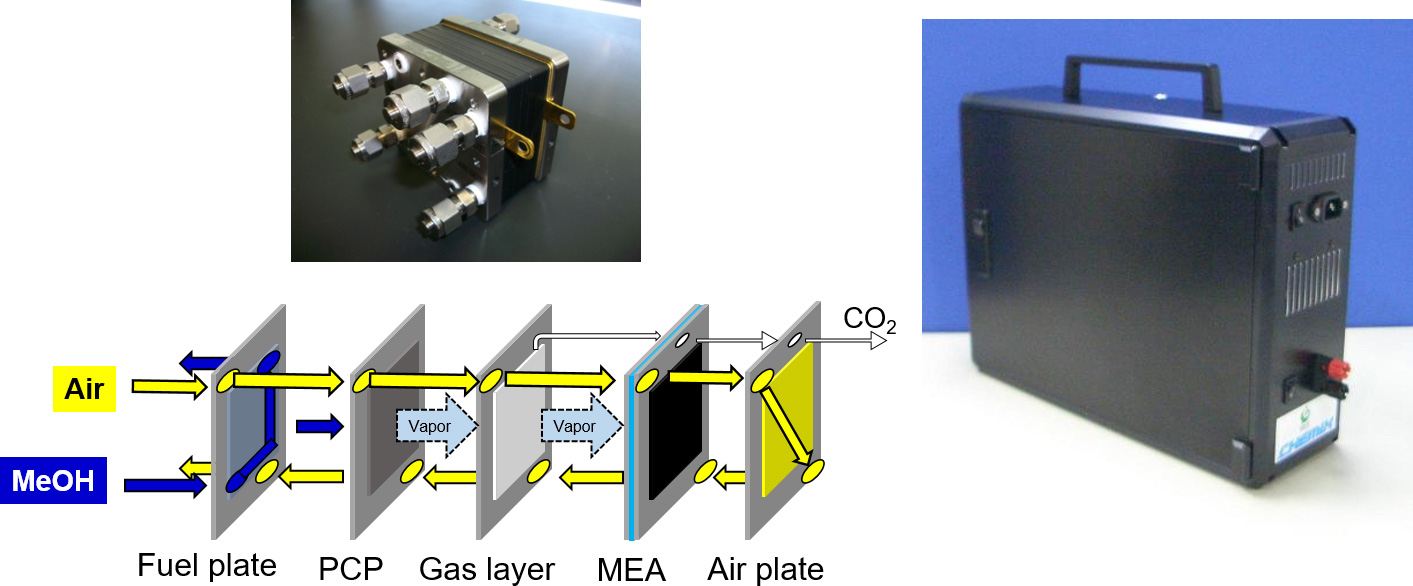
【高濃度メタノールを利用するメタノール燃料電池】
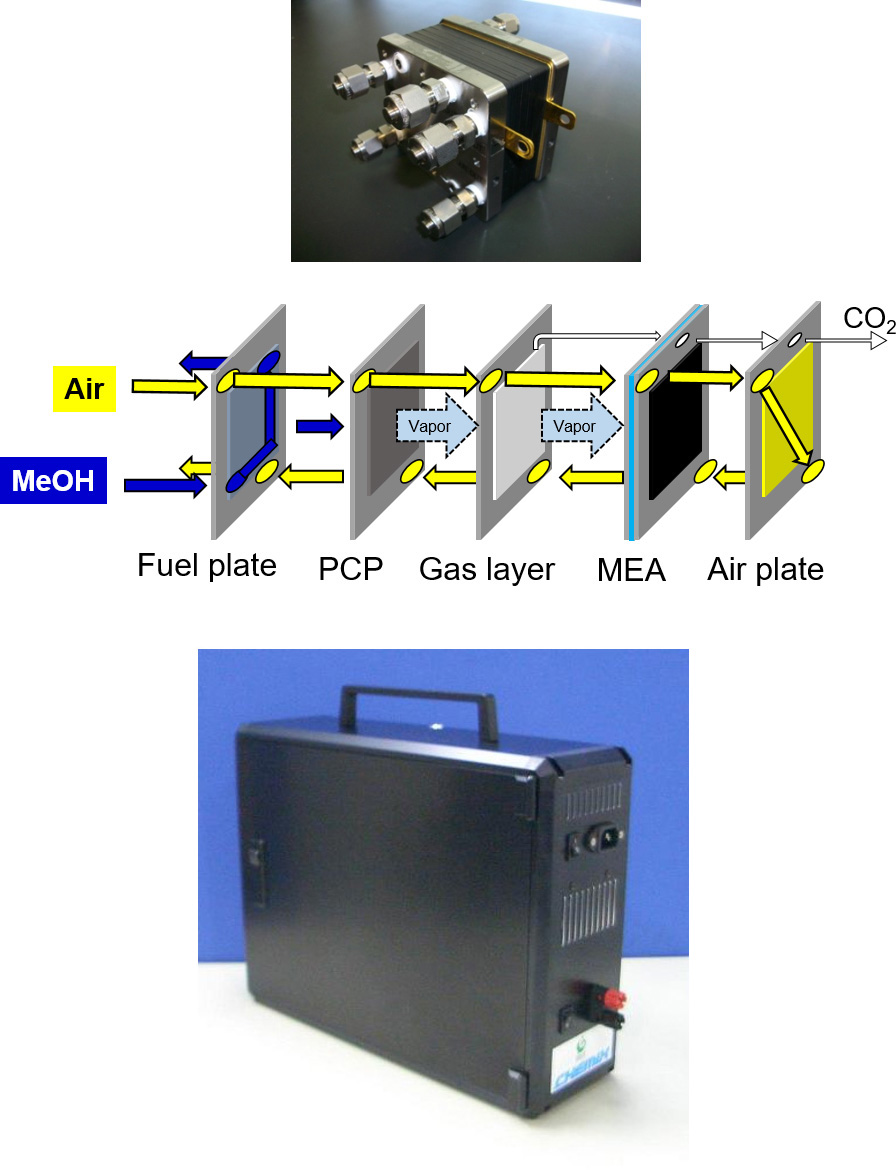
【高濃度メタノールを利用するメタノール燃料電池】
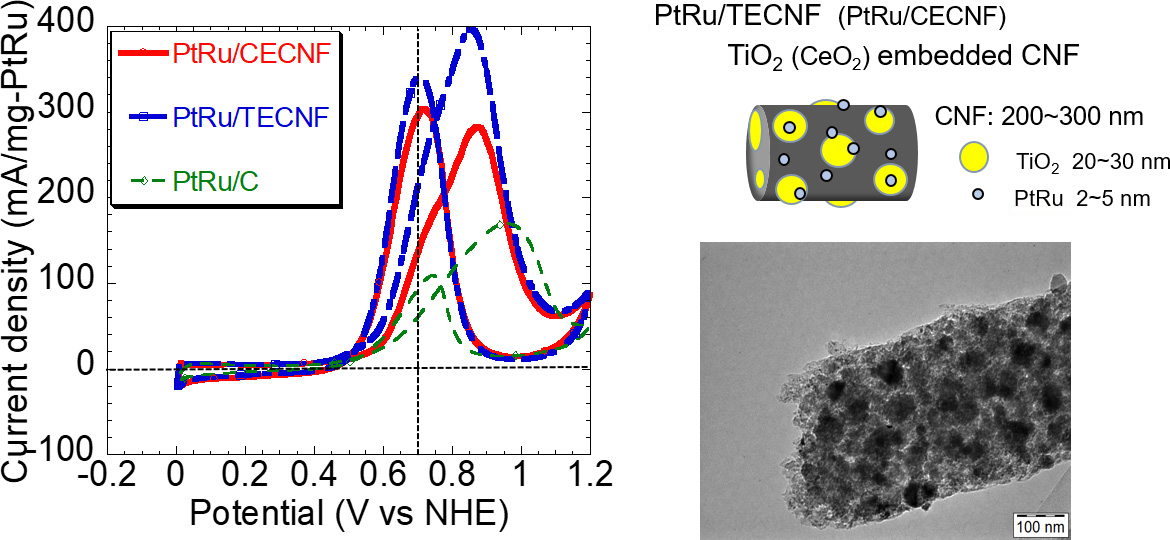
【PtRu/TECNF触媒とその活性比較】
DMFCは水素燃料電池に比べ出力が低く、その出力を上げることが課題の一つです。出力増大のために、過電圧が大きい燃料極でのメタノール酸化反応を活性化させる触媒の開発を行っています。触媒の担体効果に着目し、PtRuの金属微粒子との相互作用を大きく期待できる担体として酸化チタンや酸化セリウムの微粒子を埋め込んだカーボンナノファイバーの担体を提案し、それらを担体とするPtRu触媒により市販の触媒に比べ数倍も高い反応活性が得られることを報告してきました。実際にその触媒を用いたDMFCで高い出力が得られることも実証しています。さらにこの研究を基にして、還元型酸化グラフェンを担体とした触媒の開発を行っています。実際の触媒層を形成したときの層構造に着目し、質量活性が高い触媒であるとともに触媒層として反応活性点密度が高く、物質移動特性に優れた層構造を実現できる触媒の開発を目指しています。
One of the issues in DMFC is the low power output compared with that of hydrogen fuel cells. In order to increase the power output of the fuel cells, a catalyst that activates the methanol oxidation reaction at the fuel electrode is necessary. Focusing on the support effect for the Pt based catalyst, we proposed a carbon nanofiber support in which nanoparticles of the metal oxide like titanium dioxide and cerium dioxide were embedded. The catalyst with this support showed a very high reaction activity compared with that of a commercial catalyst. Currently, another material like reduced graphene oxide and its composites are investigated as alternative supports for more active catalysts.
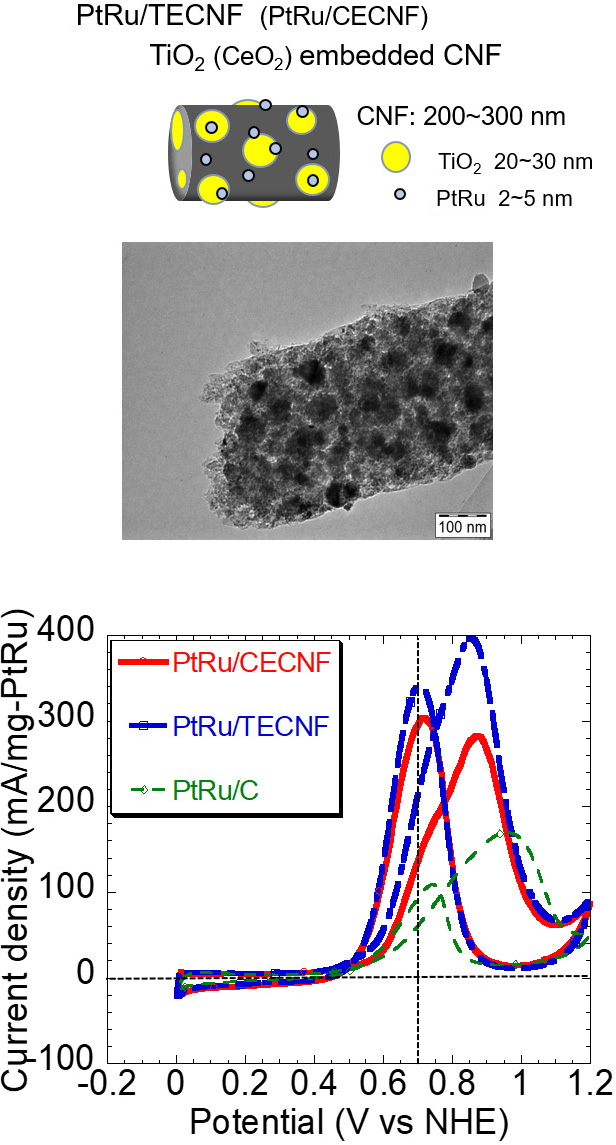
【PtRu/TECNF触媒とその活性比較】
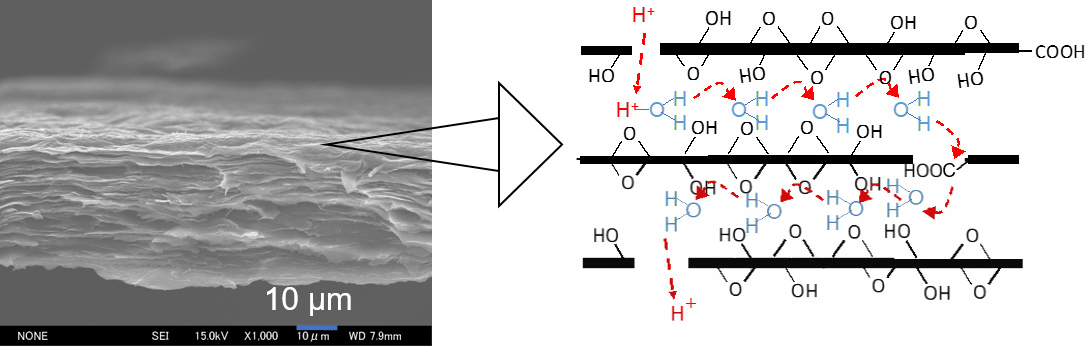
【酸化グラフェン膜の断面とプロトン導電機構の模式図】
燃料電池用プロトン導電膜として用いられているパーフルオロスルフォン酸系の高分子電解質膜は高価であり、また低湿度条件では導電率が低いという課題があります。さらにDMFC用としてはメタノール透過性が高いことも従来から残されている課題です。酸化グラフェンシートの積層膜である酸化グラフェン(GO)膜ではGOシートの表面の含酸素官能基を介してのプロトン導電性が出現します。その導電メカニズムは高分子膜の場合と異なりホッピング機構と考えられており、メタノール透過性を抑制で得きる可能性があると考えられます。一方、そのプロトン導電率については高分子膜に比べて1桁程度低く、導電率の向上が必要です。当研究室では新規な燃料電池電解質膜としてGO膜に着目し、プロトン導電率の向上と燃料透過性の低減に向けた検討を行っています。これまでGO膜へのいくつかのスルホン酸基含有化合物の修飾による導電率の向上とGOの高度酸化処理による導電率および動作安定性の向上が得られることを報告してきました。
Perfluorosulphonic acid-based polymer electrolyte membranes used in the current fuel cells are expensive, and their conductivity is not enough under low humidity conditions. Furthermore, the high methanol permeability of the electrolyte membrane in DMFC is a remaining big issue. Graphene oxide (GO) membrane which is a laminated film of GO sheets shows a relatively high proton conductivity via the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the GO sheets and the laminated structure is expected to protect the fuel permeation. We focus on the GO membrane as an alternative electrolyte membrane with a high proton conductivity and a low fuel permeability.
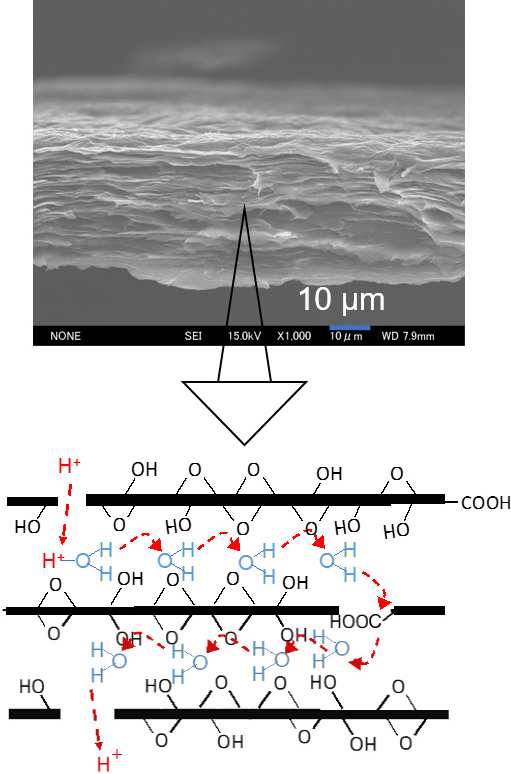
【酸化グラフェン膜の断面とプロトン導電機構の模式図】
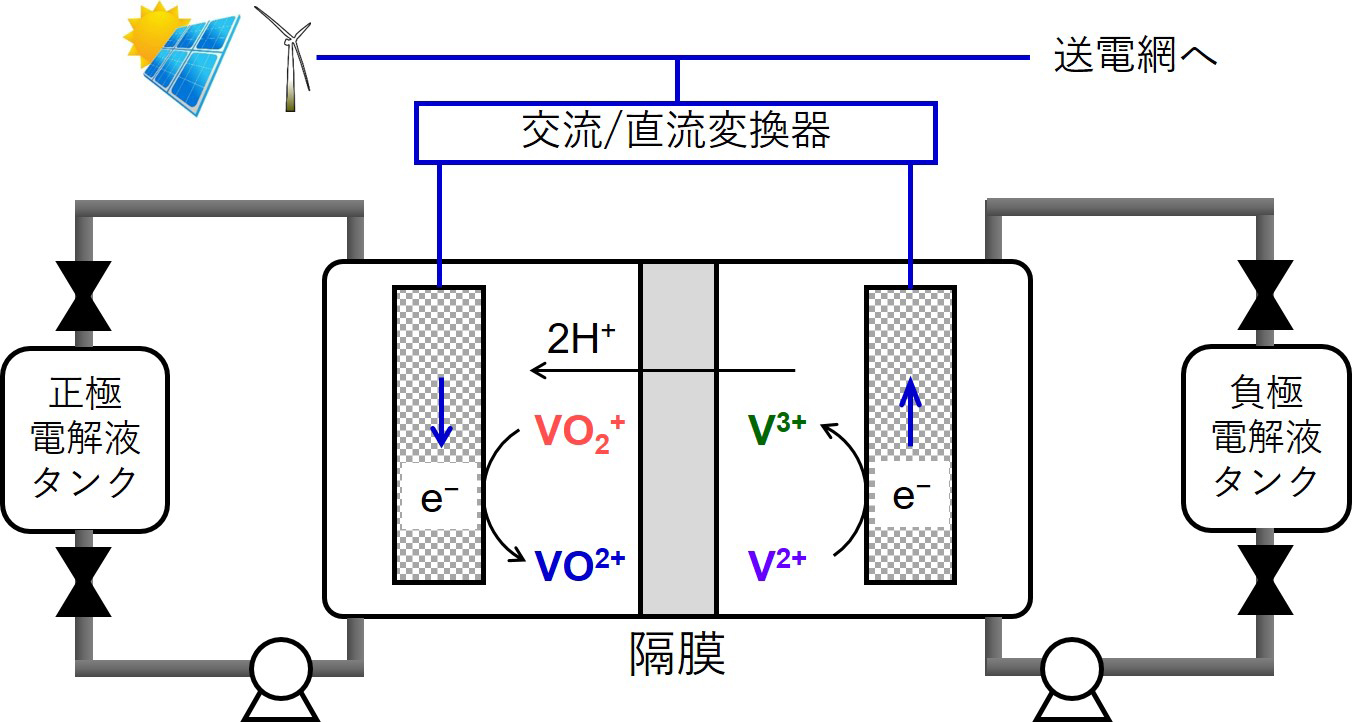
【レドックスフロー電池の構成】
太陽光・風力などの再生可能エネルギーは、エネルギーの需給ミスマッチや天候による出力変動が電力システムに悪影響をおよぼす課題があります。加えて、再生可能エネルギー発電所の特性に応じて「貯蔵エネルギー量」と「エネルギー変換速度」について高い自由度で設計したい要求があります。レドックスフロー電池は活物質(充放電する物質)を電解液に溶解させて送液するレドックスフロー電池(以下、フロー電池)は、活物質を外部タンクに貯蔵するため「貯蔵エネルギー量」と「エネルギー変換速度」を独立に設計できる等の利点から注目されています。一方で、フロー電池の既往電極材料の電極活性(反応速度)が低い点、活物質の供給(物質輸送)のしにくさ、圧力損失(液透過のしにくさによる損失)が高いために内部エネルギー損失が大きい点が実用上の課題になっています。当グループではフロー電池を反応デバイスと捉え、電極構造が損失の要因に与える影響の解明を目的に、実験・シミュレーションの両面で研究を行っています。最近では、連通孔構造が均一な(スポンジのような構造だと思っても良いでしょう)シームレスカーボン材料に注目し、反応速度の向上や圧力損失に関する実験式の提出を行っています。研究内容が多岐にわたるため、外部の大学・国立研究所・企業との共同研究を通じて課題解決を加速化させています。
Some of the renewable energy, i.e., solar, wind, etc., is intermittent by the weather, thus adjusting power and load-leveling by the electrochemical devices is required to stabilize the grid. We are studying vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), which has important characteristics such as (a) decoupled power rating and energy storage capacity, (b) accurate monitoring of the state of charge during operation, (c) viable to be grid-scale energy storage, etc. In contrast, the relatively high internal resistances, i.e., kinetic resistance, mass transport resistance, ohmic resistance, and pressure drop, are needed to be reduced. We are trying both experiments and simulations to develop novel electrode materials and membranes with collaborators in universities, institutes, and companies.

【レドックスフロー電池の構成】

【フローキャパシタの実験の様子】
今後に再生可能エネルギーを大量導入する際には天候により、電力卸売価格が大きく変動する懸念があります。近年の電力卸売市場では春季・秋季の晴天時など低需要時には5円 kWh−1以下の低い電力取引価格である一方、冬季悪天候時には50円 kWh−1以上の高い電力取引価格例もあり、再生可能エネルギーの導入とセットで天候による出力変動を平準化するデバイスの導入が必要です。上記のレドックスフロー電池と類似しながらも異なる蓄電デバイスとして、流動型のキャパシタ(電気二重層容量によって蓄電するデバイス)の研究を行っています。キャパシタは蓄電池と比べて蓄えられるエネルギーは少ないものの電流が比較的に高い利点があります。比較的に安価で資源制約の無い材料(活性炭や多孔膜など)を使い、天候変動に追従する高速応答や放電容量の自在な設計の実現を目指します。フローキャパシタもカーボン分散液の流動状態の把握、活性炭の設計、自己放電の評価など、様々な分野にまたがる研究が必要なため、外部と連携して研究を加速化しています。
The large-volume introduction of renewable energy may destabilize the price of electric power by weather and climate. Thus, the installation of not the power station of renewable energy but energy storage device is essential for society. We are studying electrochemical flow capacitors, in which active carbon particles flow in the device. The targets of research and development are (a) a high rate of charge/discharge current and (b) decoupled current and stored energy. Our group has an interest in the flow and contact of carbon particles, design of active carbon, phenomena of self-discharge, etc.

【フローキャパシタの実験の様子】